Module 3
VALUE PROPOSITION
The purpose of this module is to help you understand what the Customer Segments are and how you can work with this in your business plan.



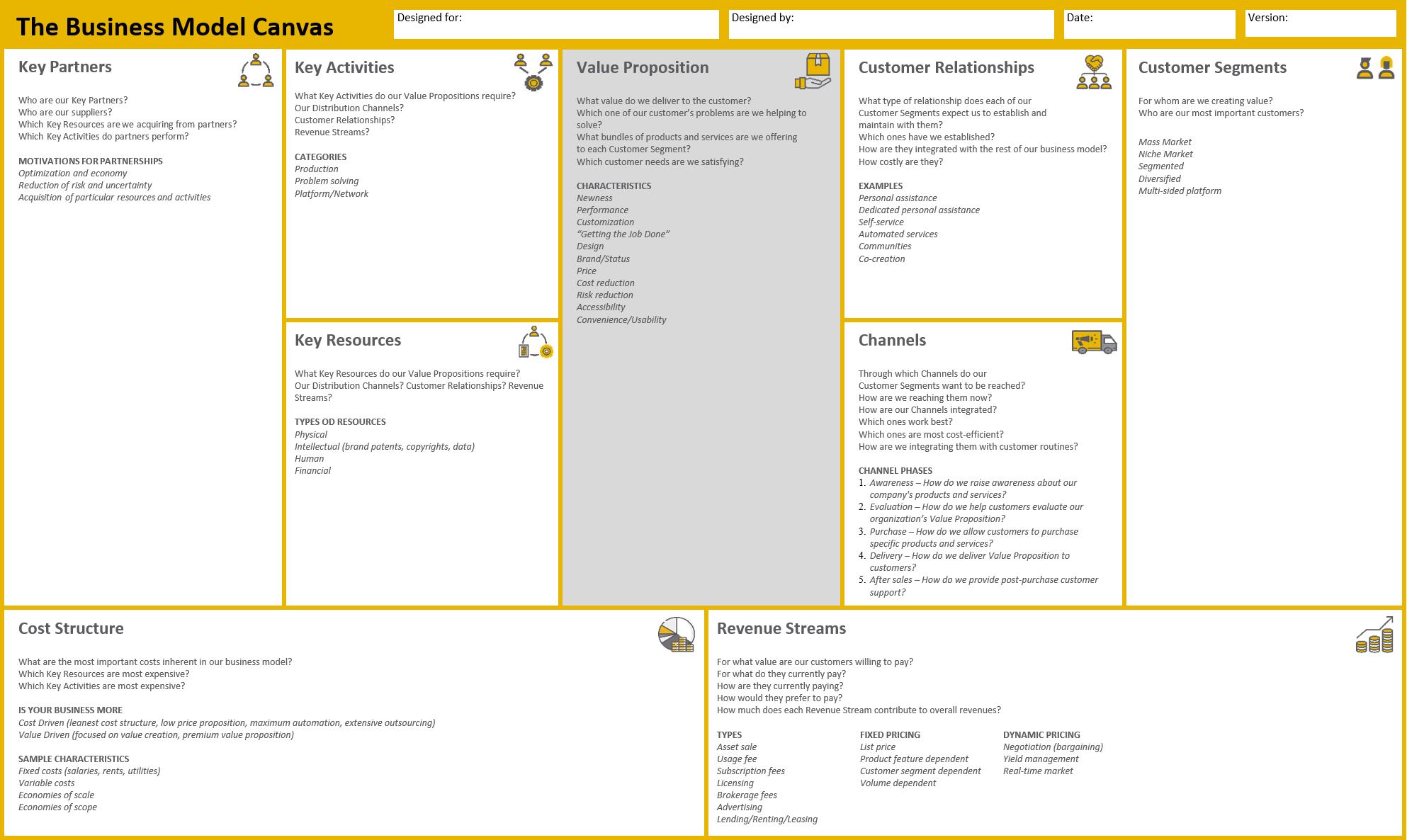
Value proposition
Introduction
The Value proposition is crucial for entrepreneurs as it describes the benefits customers can expect from products and services. One or more value propositions may apply to a product or service. The value proposition provides value through various elements, e.g., design, price, functionality, etc.
Purpose
The purpose of the Value Proposition Module is to support entrepreneurs and companies to identify value proposition, which are significant for their potential clients.
Learning Outcomes
After the completion of this module the learner will be able to:
-
- define the concept of value proposition;
- indicate the elements of value proposition;
- identify types of values proposition;
- place the value proposition in the business model;
- provide examples of some of the most popular value propositions on the market;
- select the most suitable value proposition to satisfy the clients.
Keywords
-
- SMEs
- business model
- profit
- interest
- relevancy
- differentiation
Theoretical background
A value proposition is a is a statement that answers the question: ‘why’ should someone do business with you?
A value proposition IS NOT an incentive, a catchphrase or a positioning statement.
In order to think about the value proposition, you must first consider the following aspects:
-
- Identify all the benefits your product offers.
- Describe what makes these benefits valuable.
- Identify your customer’s main problems and needs.
- Connect this value to your buyer’s problems and needs.
- Differentiate yourself as the preferred provider of this value.
The role of value proposition
Having an easily communicated and recognisable value proposition is increasingly important in today’s world where people are bombarded with an overload of information from a variety of media sources and where there are numerous competitors for a company’s business.
Successful firms craft their unique value proposition prior to entering the marketplace and they design their business operations in accordance with their value proposition.
Key elements of value proposition
-
- Newness
- Performance
- Customization
- Design
- Brand/ Status
- Price
- Cost Reduction
- Risk Reduction
- Accessibility
- Convenience/ Usability
Some explanations:
-
- Performance – better performance has been the hallmark of many product offerings over the years, with most industries managing to thrive for decades on improved performance versions of the same products.
- Customization – today’s consumers believe in self-expression and individualism. They expect the products they use to be an extension of their personality and a medium through which they can communicate their values and priorities to the world.
- Risk Reduction – the less risk associated with purchasing a product or service, the more value a customer derives from it. A reduction of the risk associated with a purchase provides peace of mind to a consumer.
Benefits of value proposition
By offering a good value proposition, companies can:
-
- Provide their customers with something unique, therefore creating differentiation and increasing competitive advantage.
- Increase the quality of their products or services.
- Gain market share.
- Improve operational efficiency.
Types of Value Proposition
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
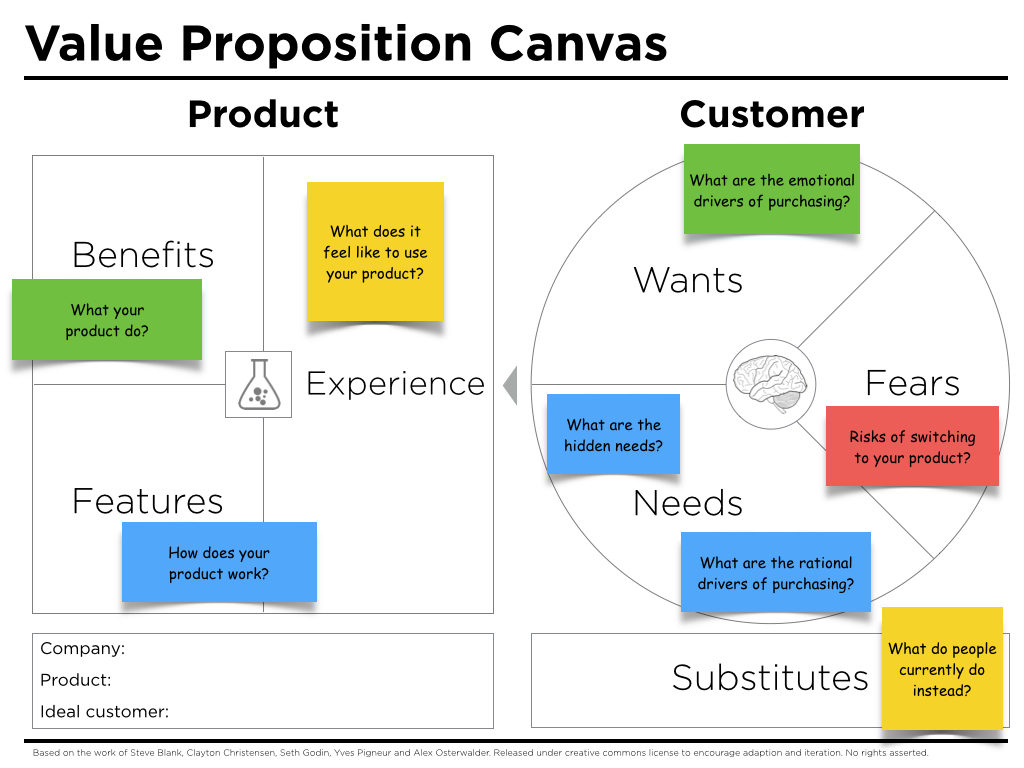 |
The value proposition should take into consideration the following aspects related to:
|
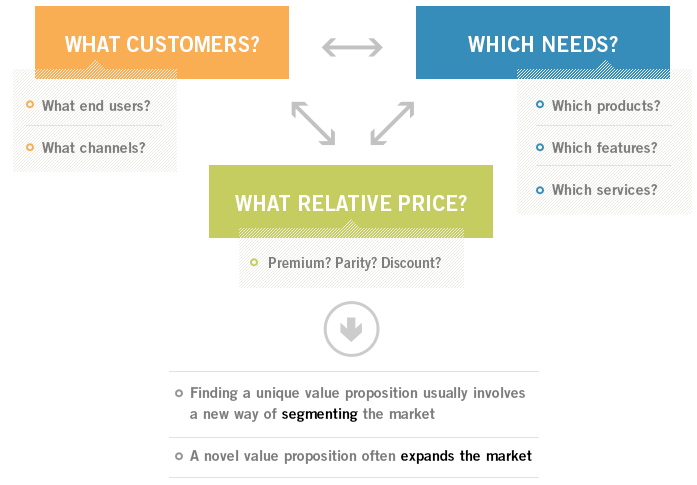
| In order to propose value proposition of high quality, it is necessary to respond to the following questions (see the Figure): (ref.: https://www.isc.hbs.edu/strategy/creating-a-successful-strategy/pages/unique-value-proposition.aspx) |
 |
Examples and Good practice
Nike’s value proposition
|
 |
|
 |
||
 |
||
Netflix’s value proposition
|
 |
|
 |
||
 |
||
Uber – The Smartest Way to Get Around
|
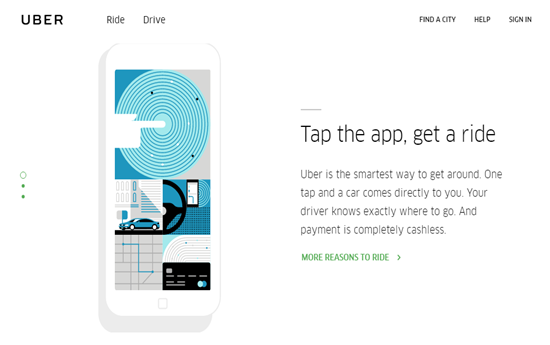 |
It directly contrasts the typical experience of getting a taxi – no phone calls to disinterested dispatchers, no painful conversations trying to explain to a stressed-out cabbie about where you need to be, and no fumbling for change or worrying you’ve got enough bills in your wallet. Just a fast, efficient way to get where you’re going. This is reinforced by the aspirational messaging towards the top of the Uber homepage, which states that “Your day belongs to you.”
Amazon’s value proposition
|
 |
|
 |
||
 |
||
KFC’s value proposition
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
References and External Links
-
- Value Proposition Canvas [accessed 21.09.2020]
https://www.peterjthomson.com/2013/11/value-proposition-canvas/
- Value Proposition Canvas [accessed 21.09.2020]
-
- Value Proposition Canvas [accessed 21.09.2020]
https://www.strategyzer.com/canvas/value-proposition-canvas
- Value Proposition Canvas [accessed 21.09.2020]
-
- How to Write a Value Proposition [accessed on 20.11.2020]
https://www.helpscout.com/blog/value-proposition-examples/
- How to Write a Value Proposition [accessed on 20.11.2020]
-
- How to Build a Web Startup [accessed on 20.11.2020]
https://steveblank.com/2011/09/22/how-to-build-a-web-startup-lean-launchpad-edition/
- How to Build a Web Startup [accessed on 20.11.2020]
Copyright @2021 – businessmodels.eu

